Introduction
After Covid-19, Pandemic and now Russia-Ukraine War, so many things happening unexpectedly😔 but thats another story lets focus on our topic for today.
In this article, we will go through how to implement Load more functionality for your next React.js project.
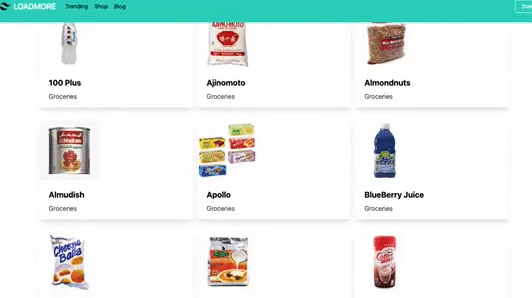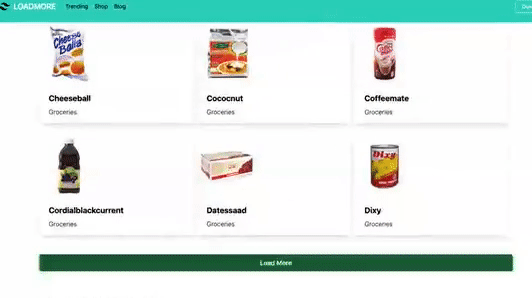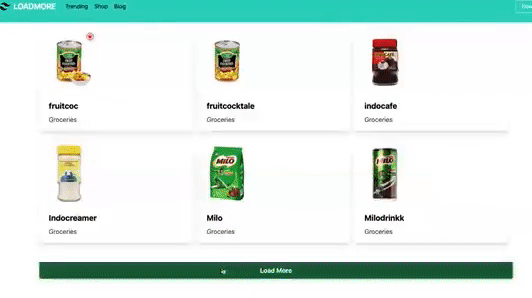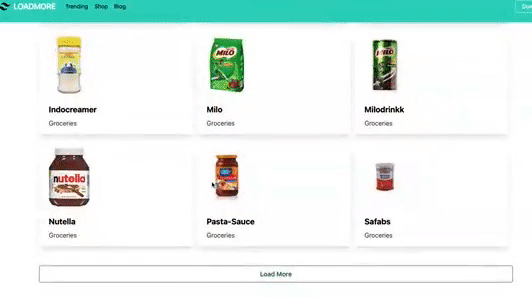
Demo of what we are working on today…👇
Why we need Load more functionality?
For example, you have an e-commerce app and you may need to load products from Rest API or from any other backend database. If we only have 10 or 20 products, it will be easy to fetch them all in just one request. However, if you have hundred and thousands of products sometime even millions, you have to implement pagination to reduce the request hitting on the server. It is important to reduce latency and server load so that the app significantly improves the performance.
So if you want display so many data such as products list, items or blog posts on your web page then you need to implement pagination. For this reason we are learning how to implement basic Load more functionality for in this article. Keep in mind in this example, we will not use any server side rending rather fetch products locally for simplicity.
Steps to implement load more pagination in React
- Create a Next.js app
- Install TailwindCSS and Configuration
- Design the app
- Implement load more button functionality
- Output
1. Create a Next.js app
Start by creating new Next.js project with TailwindCSS. The quickest way to start using Tailwind CSS in your Next.js project is to use the Next.js + Tailwind CSS Example.
npx create-next-app load-more
cd load-more
2. Install TailwindCSS and Configuration
Install tailwindcssand its peer dependencies via npm, and then run the init command to generate both tailwind.config.js and postcss.config.js.
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
npx tailwindcss init -p
Configure your template paths
module.exports = {
content: [
"./pages/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}",
"./components/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx}",
],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
}
Add the Tailwind directives to your CSS
Add the @tailwinddirectives for each of Tailwind’s layers to your ./styles/globals.css file.
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;
3. Design the app
Now let’s design the app. We will display list of groceries on the home page. Each product consists of item name, category and image. We will create few components and pages. We start with index.js page. This is main file for our app because it consists of <FreshProd /> component which is responsible to display all the products.
import Head from "next/head";
import Image from "next/image";
import Link from "next/link";
import FreshProd from "../components/FreshProd";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className="container mx-auto px-8 sm:px-12">
<section className="py-4">
<div className="flex items-center justify-between">
<h2 className="text-md sm:text-2xl font-extrabold py-8">
Stock Up on Fresh Favorites
</h2>
<Link href="/shop">
<a className="text-base py-8 cursor-pointer text-black">See All</a>
</Link>
</div>
<FreshProd />
</section>
<section className="py-4">
<h2 className="text-2xl font-extrabold py-8">Recommended Products</h2>
<FreshProd />
</section>
</main>
);
}
As said before we will use all the data locally therefore we left all the data in FreshProd.js component as an object. All the images are also stored in images folder for simplicity. We will fetch data using an external APIs or maybe from firebase database later in another tutorial.
const freshProds = [
{
id: "1",
src: "/images/100p.jpeg",
name: "100 Plus",
category: "Groceries",
},
{
id: "2",
src: "/images/Ajinomoto.jpeg",
name: "Ajinomoto",
category: "Groceries",
},
{
id: "3",
src: "/images/Almondnuts.jpg",
name: "Almondnuts",
category: "Groceries",
},
];
Now, store this object in a map so we can display them on <Product /> component. For that we need to Destructuring Props.
function FreshProd() {
return (
<div>
<div className="grid grid-cols-3">
{freshProds?.map((freshprod) => (
<Product
key={freshprod.id}
src={freshprod.src}
name={freshprod.name}
category={freshprod.category}
/>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default FreshProd;
Up to this point, we are able to view all the products in Product component.
import React from "react";
import Image from "next/image";
function Product({ id, name, src, category }) {
return (
<div className="py-4">
<div className="max-w-sm rounded overflow-hidden shadow-lg">
<Image
className="rounded-md"
objectFit="fill"
src={src}
width={150}
height={150}
/>
<div className="px-6 py-4">
<div className="font-bold text-xl mb-2">{name}</div>
<p className="text-gray-700 text-base">{category}</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default Product;
Now let’s try to write a function so that it display certain amount of products instead of displaying all the products on the screen. This is where we use Loadmore button and implement pagination on our app. In this case we want to display 6 products.
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(6);
const showMoreItems = () => {
setVisible((prevValue) => prevValue + 6);
};
Lastly we slice the object, so in each time we press the button it will display 6 products on the screen. We use props to pass the data to Product component.
<div className="grid grid-cols-3">
{freshProds?.slice(0, visible).map((freshprod) => (
<Product
key={freshprod.id}
src={freshprod.src}
name={freshprod.name}
category={freshprod.category}
/>
))}
</div>
This is the button which is used to load more products on each click.
<div className=" flex flex-col pt-8 ">
<button
className=" content-between bg-transparent hover:bg-green-800
text-green-800 font-semibold hover:text-white py-2 px-4 border
border-green-800 hover:border-transparent rounded"
onClick={showMoreItems} >
Load More
</button>
</div>
Wrap Up
Thats it! Now we have implemented simple pagination or loadmore functionlity on our Next.js app project. We can improve this functionality and code but this is a good starting point.
Code
You can find the source code Github